monohybrid cross - A monohybrid cross is a breeding experiment between parental generation organisms that differ in one trait.
Mendel's law of segregation states that allele pair separate or segregate during gamete formation and randomly unite at fertilization so that offspring acquire one factor from each
parent.
Ratio of F2 generation is 3:1 This allele pair is for the same trait. eg TT and tt
Diagram of monohybrid cross
/1.GENETIC%20BASIS%20OF%20INHERITANCE/image/2.png)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
dihybrid cross - A dihybrid cross is a breeding experiment between parental generation organisms that differ in one trait.
Mendel's law of independent assortment states that allele pairs separate independently during the formation of gametes so traits are transmitted to offspring independently of on another.
This ratio is 9:3:3:1
This allele pair is for different traits eg. BBAA, BbAa, Bbaa
Diagram of Mendel dihybrid cross
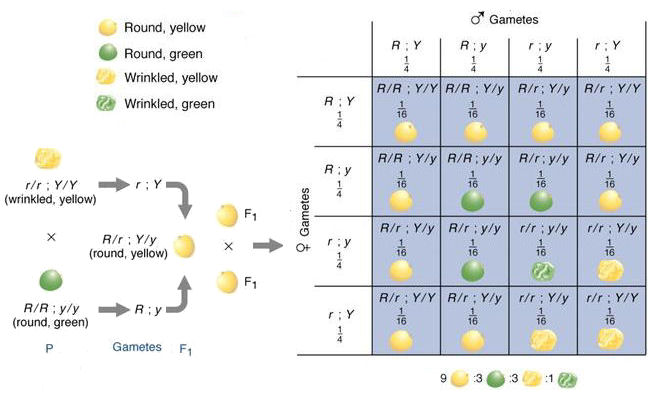
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Sex linkages - some genes are sex linked because their inheritance is affected by whether a person is male or female.
Women have two X chromosomes while men have a X and Y chromosome.
The X chromosome is much larger than the Y chromosome. So the X chromosome carry more genes therefore some genes on the X chromosome is absent on the Y chromosome
Example - hemophilia. factor VIII, a protein is needed to enable blood to clot. The recessive allele (small h) codes for haemophilia. This gene is only carried on the X chromosome
Diagrams showing possible phenotypes and genotypes

A foetus that is homozygouse does not develop as this genotype is lethal so no babies are born with it. Haemophilia causes bleeding into joints and other parts of the body.This is very painful but it can be treated by giving the person factor VIII.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Codominant - where both alleles contribute to the phenotype of the heterozygous plant.
When a pure bred white flower is cross with a pure bred red flower all the first generation will have all pink flowers.
When all pink flowers are interbred they give the ratio 1:2:1.
Diagram showing codominance

so in codominance there is more variation as it give 3 colours because the red allele is not dominant to white allele and white allele is not dominant to red allele
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Multiple allele - where genes have more than two alleles
At the human ABO blood group locus there are 3 alleles. The gene locus is I and it has 3 alleles A B and O. A and B are codominant. A is dominant to O and B is dominant to O.
There are 6 genotypes and 4 phenotypes (blood types)
Diagram showing genotypes and phenotypes

-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Epistatis - interaction between genes at different loci in which the expression of a gene is influenced by another.
The epistatic gene CC or Cc determines if colour is present
The ratio is 9:3:4
CC or Cc is colour cc is albino
Bb or BB is black
bb is brown
Diagram showing test cross with epistasis
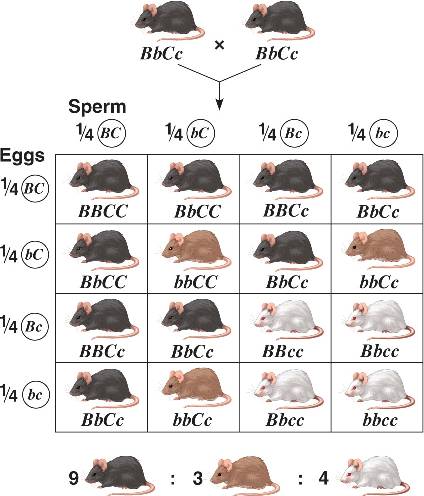
For colour to be produced there must be a dominant C or two; recessive (cc) is albino
For black to be produced there must be a dominant B. So Bb or BB with at least one C is black.
For brown to be produced there must be recessive bb with at least one C is brown